How SSL Certificates Work
An SSL Certificate, or Secure Socket Layer, is a commonly used protocol for managing the security of data transmission and communication on the Internet.
These certificates contain unique, authenticated information about the owner, so that when a secure online transaction takes place the owner is verified, the
customer authenticated, and a unique session key establishes encryption. This secure session is what enables your customers' privacy.
Any sensitive information you gather from users should be protected by SSL. Sensitive data not only includes credit card or other payment information; it includes
any forms where your visitors can enter their name, address, contact information, or passwords.
In addition to protecting your visitors from fraud, using an SSL Certificate can instill confidence in your users, boosting your sales and increasing your credibility.
What Your Visitors See
You may already be familiar with sites using SSL Certificates. Upon entering a secure area, a web page secured by SSL will use the protocol "https"
(Hypertext Transfer Protocol over Secure Socket Layer) instead of "http" (Hypertext Transfer Protocol).
Another indicator of SSL is a lock icon, which displays in most browsers, generally in the address or status bar. Some browsers, including Firefox, will also turn the address bar yellow.
Additionally, when you purchase your SSL Certificate from DomainIt, you can display a TrustLogo throughout your site. This will alert your visitors that your site is secure where necessary.
Compare SSL Plan Features

The lock indicates a page secured by SSL. The appearance of this varies depending on the type of browser, and may be located in the address bar, status bar, or both.
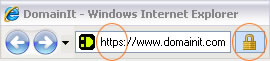
https stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol over Secure Socket Layer, indicating the use of an SSL Certificate.